Cart 0 Product Products (empty)
No products
Free shipping! Shipping
$0.00 Total
Product successfully added to your shopping cart
Quantity
Unit
Total
There are 0 items in your cart. There is 1 item in your cart.
Total products (tax excl.)
Total shipping (tax excl.) Free shipping!
Total (tax excl.)
Metabolites
- Protein Control Ligand
- Pathway Inhibitors
- Enzyme Inhibitors
- Kinase Inhibitors
- Protease
- Synthase
- p18
- p38
- p53
- p70
- p90
- Peptidase
- Carboxyl and Decarboxylases
- Ceramide Turnover Enzymes
- Chromatin Modifying Enzymes
- Cyclic Nucleotide Turnover Enzymes
- Glycerophospholipid Turnover Enzymes
- Hydroxylases
- Ubiquitin-Activating Enzyme
- Adenosine Deaminase
- Clathrin
- Nuclease
- p68
- ACE
- COX
- DHFR
- Neprilysin
- NF-κB
- RAF
- RAS
- Reductase
- ROR
- Topoisomerase
- Transferase
- Protein Inhibitors
- Transporter Inhibitors
- Cell Inhibition
- Synthase
- Receptor Tyrosine Phosphatases (RTP)
- AChE
- Peptidase
- Autophagy
- Toll-Like Receptor (TLR)
- Enzyme Inhibitors
- Function Modulators
- Activators
- G Protein-Coupled Receptor Ligands
- 5HT Receptors
- Adrenoceptor
- Angiotensin Receptor
- Cannabinoid Receptors
- CCK Receptors
- DA Receptors
- EAA Receptors
- Ghrelin Receptors
- GABA Receptors
- Histamine Receptors
- Leukotriene Receptors
- Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors
- Motilin Receptors
- Muscarinic Receptor
- Neuropeptide Receptors
- Opioid Receptors
- Orexin Receptors
- Orphan Receptors
- Prostanoid Receptors
- Proteinase-Activated Receptors
- Purinergic Receptors
- Ryanodine receptor
- Sigma Receptors
- Thrombin Receptor
- Vaniloid Receptor
- VIP and PACAP Receptors
- Neurotensin Receptors
- Urotensin Receptor
- Imidazoline receptor
- SMO Receptors
- Apelin Receptor
- β-arrestin/β2-adaptin
- KDM4
- Glucocorticoid Receptor
- Laminin Receptor
- AHR
- Amylin Receptor
- Bombesin Receptor
- Bradykinin Receptor
- CFTR
- CGRP Receptor
- CRFR
- Endothelin Receptor
- Ephrin Receptor
- Farnesoid X receptor (FXR)
- Glucagon Receptor
- Nuclear Receptor Ligands
- GDNF Receptors
- TNF Receptors
- Transcription Factors
- Chemokines
- Cytokine Receptors
- Biomarkers and Buffer Solutions
- Molecular Probes
- Stem Cell Research
- Alzheimer's Disease
- Apoptosis
- Cancer Research
- Epigenetics
- Metabolites
- PET/SPECT Imaging Precursors
- Customized Screening Library
- Ultra Pure Pharmacological Standard
- Tissue Microarray (TMA)
- Proteins and Antibodies
- Primary Cells
- ELISA KIT
- Natural Products
- Lab Equipments
- Humanized Mice for PDX Platform
- Rare Chemicals
- Custom Synthesis
- Antibacterial
- Antifungal
- Antioxidant
- Antiviral
- Molecular Glues
- PROTAC Linker
- SARS-CoV
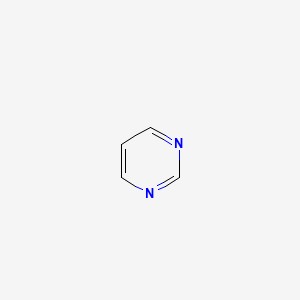 View larger
View larger Data sheet
| Molecular Formula | C4H4N2 |
| Molecular Weight | 80.09 |
| CAS Numbers | 289-95-2 |
| Storage Condition | 0C Short Term, -20C Long Term |
| Solubility | DMSO |
| Purity | 98% by HPLC |
| SMILES Code | C=1C=NC=NC1 |
| References | Loffler M, et al. Pyrimidine pathways in health and disease. Trends Mol Med. 2005 Sep;11[9] 430-7. |
More info
Pyrimidine (Metadiazine)s are heterocyclic, six-membered, nitrogen-containing carbon ring structures, with uracil, cytosine and thymine being the basal structures of ribose-containing nucleosides (uridine, cytidine, and thymidine respectively), or deoxyribose-containing deoxynucleosides, and their corresponding ribonucleotides or deoxyribonucleotides. Pyrimidines serve essential functions in human metabolism as ribonucleotide bases in RNA (uracil and cytosine), and as deoxyribonucleotide bases in DNA (cytosine and thymine), and are linked by phosphodiester bridges to purine nucleotides in double-stranded DNA, in both the nucleus and the mitochondria. Pyrimidine activated sugars are also involved in polysaccharide and phospholipid synthesis, glucuronidation in detoxification processes, glycosylation of proteins and lipids and in the recently identified novel endothelium-derived vasoactive dinucleotides.