No products
Product successfully added to your shopping cart
There are 0 items in your cart. There is 1 item in your cart.
Primary Cells
- Protein Control Ligand
- Pathway Inhibitors
- Enzyme Inhibitors
- Kinase Inhibitors
- Protease
- Synthase
- p18
- p38
- p53
- p70
- p90
- Peptidase
- Carboxyl and Decarboxylases
- Ceramide Turnover Enzymes
- Chromatin Modifying Enzymes
- Cyclic Nucleotide Turnover Enzymes
- Glycerophospholipid Turnover Enzymes
- Hydroxylases
- Ubiquitin-Activating Enzyme
- Adenosine Deaminase
- Clathrin
- Nuclease
- p68
- ACE
- COX
- DHFR
- Neprilysin
- NF-κB
- RAF
- RAS
- Reductase
- ROR
- Topoisomerase
- Transferase
- Protein Inhibitors
- Transporter Inhibitors
- Cell Inhibition
- Synthase
- Receptor Tyrosine Phosphatases (RTP)
- AChE
- Peptidase
- Autophagy
- Toll-Like Receptor (TLR)
- Enzyme Inhibitors
- Function Modulators
- Activators
- G Protein-Coupled Receptor Ligands
- 5HT Receptors
- Adrenoceptor
- Angiotensin Receptor
- Cannabinoid Receptors
- CCK Receptors
- DA Receptors
- EAA Receptors
- Ghrelin Receptors
- GABA Receptors
- Histamine Receptors
- Leukotriene Receptors
- Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors
- Motilin Receptors
- Muscarinic Receptor
- Neuropeptide Receptors
- Opioid Receptors
- Orexin Receptors
- Orphan Receptors
- Prostanoid Receptors
- Proteinase-Activated Receptors
- Purinergic Receptors
- Ryanodine receptor
- Sigma Receptors
- Thrombin Receptor
- Vaniloid Receptor
- VIP and PACAP Receptors
- Neurotensin Receptors
- Urotensin Receptor
- Imidazoline receptor
- SMO Receptors
- Apelin Receptor
- β-arrestin/β2-adaptin
- KDM4
- Glucocorticoid Receptor
- Laminin Receptor
- AHR
- Amylin Receptor
- Bombesin Receptor
- Bradykinin Receptor
- CFTR
- CGRP Receptor
- CRFR
- Endothelin Receptor
- Ephrin Receptor
- Farnesoid X receptor (FXR)
- Glucagon Receptor
- Nuclear Receptor Ligands
- GDNF Receptors
- TNF Receptors
- Transcription Factors
- Chemokines
- Cytokine Receptors
- Biomarkers and Buffer Solutions
- Molecular Probes
- Stem Cell Research
- Alzheimer's Disease
- Apoptosis
- Cancer Research
- Epigenetics
- Metabolites
- PET/SPECT Imaging Precursors
- Customized Screening Library
- Ultra Pure Pharmacological Standard
- Tissue Microarray (TMA)
- Proteins and Antibodies
- Primary Cells
- ELISA KIT
- Natural Products
- Lab Equipments
- Humanized Mice for PDX Platform
- Rare Chemicals
- Custom Synthesis
- Antibacterial
- Antifungal
- Antioxidant
- Antiviral
- Molecular Glues
- PROTAC Linker
- SARS-CoV
 View larger
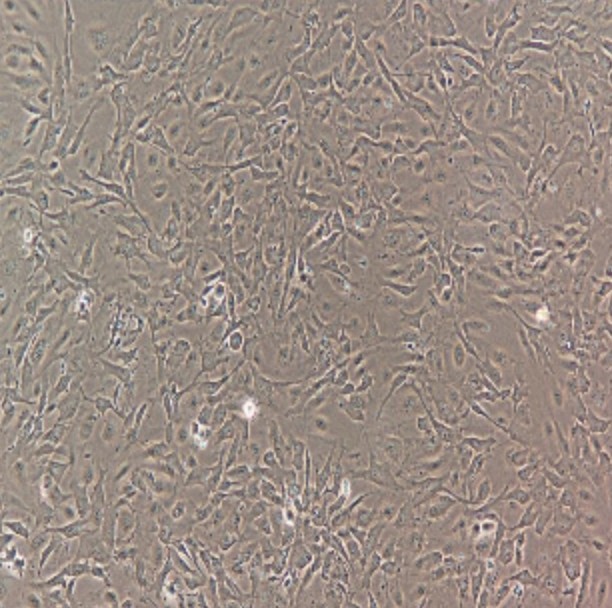
View larger Human Primary Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells
HUM-d018
Each vial contains >5x105 cells in 1mL volume
1000 Items
Molarity Calculation Cart®
HOW TO ORDER
More info
Cell Details
The sinusoidal endothelial cells are the most abundant cells in the liver non-parenchymal cells, accounting for about 70% of the total number of non-parenchymal cells in the liver. They are significantly different in phenotype and function from ordinary capillary endothelial cells. There is no intercellular connection between the sinusoidal endothelial cells, and there are few substances in the basement membrane under the cells. Therefore, the sinusoidal permeability is high, which is beneficial to regulate the substance exchange.
Unlike the self-replication of hepatocytes, the new LSECs in liver regeneration mainly come from the differentiation of other cellular components inside and outside the liver. Many studies have confirmed the bone marrow-derived substitution of LSECs during liver regeneration. Endothelial progenitor cells are the major cellular components involved in this process.
Aperture is the most characteristic structure of sinusoidal endothelial cells, from <10nm to 1~2μm range, since under physiological conditions in the presence and absence of endothelial fenestration complete base structure of the membrane, composed of a sinusoidal endothelial cells The wall of the hepatic sinus is the only capillaries in the capillary wall of the whole body that lack the basement membrane. Except for the blood cells in the sinus, the plasma components can enter the Disse gap from the window to exchange material.
Cell Characteristics
1) The cells are derived from human normal liver tissue.
2) Cell identification: von von Willebrand factor (vWF) was positive for immunofluorescence staining.
3) The purity of the identified cells is higher than 90%.
4) Does not contain HIV-1, HBV, HCV, mycoplasma, bacteria, yeast, and fungi.
5) Cell growth mode: epithelioid, polygonal cells, adherent culture.
Transportation and Preservation
Depending on the weather conditions and the distance of transportation, the company negotiates with the customer and chooses one of the following methods.
1) 1mL of frozen cell suspension is placed in a 1.8mL cryotube and placed in a foam incubator filled with dry ice for transport; after receiving the cells, thaw the resuscitated cells as soon as possible for culture. If resuscitation is not possible immediately, Cryopreserved cells can be stored at -80°C for 1 month.
2) T-25 culture flask is filled with complete medium and then transported at room temperature. After receiving the cells, please observe the growth state of the cells under a microscope. If the bottle filling rate exceeds 85%, please carry out the subculture immediately. If there are more cells in suspension, allow the flask to stand overnight in the incubator to help the undead suspension cells to reattach.
Product Use
1) This product can only be used for scientific research
2) This product has not passed the audit for living animals and humans directly.
3) This product has not passed the audit for in vivo diagnosis.

