No products
Product successfully added to your shopping cart
There are 0 items in your cart. There is 1 item in your cart.
Proteins and Enzymes
- Protein Control Ligand
- Pathway Inhibitors
- Enzyme Inhibitors
- Kinase Inhibitors
- Protease
- Synthase
- p18
- p38
- p53
- p70
- p90
- Peptidase
- Carboxyl and Decarboxylases
- Ceramide Turnover Enzymes
- Chromatin Modifying Enzymes
- Cyclic Nucleotide Turnover Enzymes
- Glycerophospholipid Turnover Enzymes
- Hydroxylases
- Ubiquitin-Activating Enzyme
- Adenosine Deaminase
- Clathrin
- Nuclease
- p68
- ACE
- COX
- DHFR
- Neprilysin
- NF-κB
- RAF
- RAS
- Reductase
- ROR
- Topoisomerase
- Transferase
- Protein Inhibitors
- Transporter Inhibitors
- Cell Inhibition
- Synthase
- Receptor Tyrosine Phosphatases (RTP)
- AChE
- Peptidase
- Autophagy
- Toll-Like Receptor (TLR)
- Enzyme Inhibitors
- Function Modulators
- Activators
- G Protein-Coupled Receptor Ligands
- 5HT Receptors
- Adrenoceptor
- Angiotensin Receptor
- Cannabinoid Receptors
- CCK Receptors
- DA Receptors
- EAA Receptors
- Ghrelin Receptors
- GABA Receptors
- Histamine Receptors
- Leukotriene Receptors
- Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors
- Motilin Receptors
- Muscarinic Receptor
- Neuropeptide Receptors
- Opioid Receptors
- Orexin Receptors
- Orphan Receptors
- Prostanoid Receptors
- Proteinase-Activated Receptors
- Purinergic Receptors
- Ryanodine receptor
- Sigma Receptors
- Thrombin Receptor
- Vaniloid Receptor
- VIP and PACAP Receptors
- Neurotensin Receptors
- Urotensin Receptor
- Imidazoline receptor
- SMO Receptors
- Apelin Receptor
- β-arrestin/β2-adaptin
- KDM4
- Glucocorticoid Receptor
- Laminin Receptor
- AHR
- Amylin Receptor
- Bombesin Receptor
- Bradykinin Receptor
- CFTR
- CGRP Receptor
- CRFR
- Endothelin Receptor
- Ephrin Receptor
- Farnesoid X receptor (FXR)
- Glucagon Receptor
- Nuclear Receptor Ligands
- GDNF Receptors
- TNF Receptors
- Transcription Factors
- Chemokines
- Cytokine Receptors
- Biomarkers and Buffer Solutions
- Molecular Probes
- Stem Cell Research
- Alzheimer's Disease
- Apoptosis
- Cancer Research
- Epigenetics
- Metabolites
- PET/SPECT Imaging Precursors
- Customized Screening Library
- Ultra Pure Pharmacological Standard
- Tissue Microarray (TMA)
- Proteins and Antibodies
- Primary Cells
- ELISA KIT
- Natural Products
- Lab Equipments
- Humanized Mice for PDX Platform
- Rare Chemicals
- Custom Synthesis
- Antibacterial
- Antifungal
- Antioxidant
- Antiviral
- Molecular Glues
- PROTAC Linker
- SARS-CoV
 View larger
View larger Mouse IL4 / Interleukin-4 Protein
51084-MNAE
Activity: Measured in a cell proliferation assay using HT-2 mouse T cells. The ED50 for this effect is typically 0.4-2 ng/mL.
1000 Items
Please ask for quote for unit smaller than 1 mg
Molarity Calculation Cart®
HOW TO ORDER
Data sheet
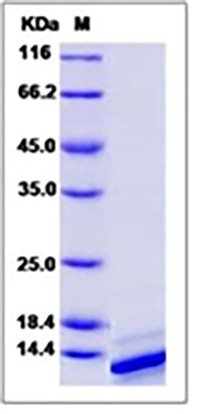
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse IL4 consists of 119 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 13.4 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 14 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| Storage Condition | Samples are stable for up to twelve months from date of receipt at -70℃. Store it under sterile conditions at -20℃ to -80℃. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Purity | 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE |
More info
Protein Construction: A DNA sequence encoding the mouse IL4 (NP_067258.1) (His23-Ser140) was expressed with a N-terminal Met.
Formulation: Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4.1. Normally 5% - 8% trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA.2. Please contact us for any concerns or special requirements.Please refer to the specific buffer information in the hard copy of CoA.
Reconstitution: A hardcopy of COA with reconstitution instruction is sent along with the products. Please refer to it for detailed information.
IL-4 Background Information: Interleukin-4, also known as IL4, is a secreted protein which belongs to the IL-4 / IL-13 family. Interleukin-4 / IL4 has many biological roles, including the stimulation of activated B-cell and T-cell proliferation. It enhances both secretion and cell surface expression of IgE and IgG1. Interleukin-4 / IL4 also regulates the expression of the low affinity Fc receptor for IgE (CD23) on both lymphocytes and monocytes. Interleukin-4 is essential for the switching of B cells to IgE antibody production and for the maturation of T helper (Th) cells toward the Th2 phenotype. It participates in at least several B-cell activation processes as well as of other cell types. However, studies show that double mutant (Q116D, Y119D) of the murine IL4 protein (QY), both glutamine 116 and tyrosine 119, which binds to the IL4 receptor alpha, completely inhibites in a dose-dependent manner the IL4-induced proliferation of lipopolysaccharide-stimulated murine splenic B-cells, of the murine T cell line CTLL-2, and of the murine pre-B-cell line BA/F3. QY also inhibited the IL4-stimulated up-regulation of CD23 expression by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated murine splenic B-cells and abolished tyrosine phosphorylation of the transcription factor Stat6 and the tyrosine kinase Jak3 in IL4-stimulated BA/F3 cells.
References:
- Grunewald SM. et al.,1998, J Immunol. 160 (8): 4004-9.
- Susanne M. et al,1997, THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY. 272 (3): 1480-3.
- Nishikubo K. et al.,2003, Gene Ther. 10 (26): 2119-25.

