No products
Product successfully added to your shopping cart
There are 0 items in your cart. There is 1 item in your cart.
Proteins and Enzymes
- Protein Control Ligand
- Pathway Inhibitors
- Enzyme Inhibitors
- Kinase Inhibitors
- Protease
- Synthase
- p18
- p38
- p53
- p70
- p90
- Peptidase
- Carboxyl and Decarboxylases
- Ceramide Turnover Enzymes
- Chromatin Modifying Enzymes
- Cyclic Nucleotide Turnover Enzymes
- Glycerophospholipid Turnover Enzymes
- Hydroxylases
- Ubiquitin-Activating Enzyme
- Adenosine Deaminase
- Clathrin
- Nuclease
- p68
- ACE
- COX
- DHFR
- Neprilysin
- NF-κB
- RAF
- RAS
- Reductase
- ROR
- Topoisomerase
- Transferase
- Protein Inhibitors
- Transporter Inhibitors
- Cell Inhibition
- Synthase
- Receptor Tyrosine Phosphatases (RTP)
- AChE
- Peptidase
- Autophagy
- Toll-Like Receptor (TLR)
- Enzyme Inhibitors
- Function Modulators
- Activators
- G Protein-Coupled Receptor Ligands
- 5HT Receptors
- Adrenoceptor
- Angiotensin Receptor
- Cannabinoid Receptors
- CCK Receptors
- DA Receptors
- EAA Receptors
- Ghrelin Receptors
- GABA Receptors
- Histamine Receptors
- Leukotriene Receptors
- Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors
- Motilin Receptors
- Muscarinic Receptor
- Neuropeptide Receptors
- Opioid Receptors
- Orexin Receptors
- Orphan Receptors
- Prostanoid Receptors
- Proteinase-Activated Receptors
- Purinergic Receptors
- Ryanodine receptor
- Sigma Receptors
- Thrombin Receptor
- Vaniloid Receptor
- VIP and PACAP Receptors
- Neurotensin Receptors
- Urotensin Receptor
- Imidazoline receptor
- SMO Receptors
- Apelin Receptor
- β-arrestin/β2-adaptin
- KDM4
- Glucocorticoid Receptor
- Laminin Receptor
- AHR
- Amylin Receptor
- Bombesin Receptor
- Bradykinin Receptor
- CFTR
- CGRP Receptor
- CRFR
- Endothelin Receptor
- Ephrin Receptor
- Farnesoid X receptor (FXR)
- Glucagon Receptor
- Nuclear Receptor Ligands
- GDNF Receptors
- TNF Receptors
- Transcription Factors
- Chemokines
- Cytokine Receptors
- Biomarkers and Buffer Solutions
- Molecular Probes
- Stem Cell Research
- Alzheimer's Disease
- Apoptosis
- Cancer Research
- Epigenetics
- Metabolites
- PET/SPECT Imaging Precursors
- Customized Screening Library
- Ultra Pure Pharmacological Standard
- Tissue Microarray (TMA)
- Proteins and Antibodies
- Primary Cells
- ELISA KIT
- Natural Products
- Lab Equipments
- Humanized Mice for PDX Platform
- Rare Chemicals
- Custom Synthesis
- Antibacterial
- Antifungal
- Antioxidant
- Antiviral
- Molecular Glues
- PROTAC Linker
- SARS-CoV
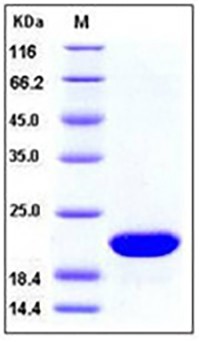 View larger
View larger Human FGF10 / KGF2 Protein
10573-HNAE
Activity: Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized humen FGF10 at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind Cynomolgus FGFR1-Fc (Cat:90075-C02H) with a linear range of 31.25-2000 ng/mL.
1000 Items
Please ask for quote for unit smaller than 1 mg
Molarity Calculation Cart®
HOW TO ORDER
Data sheet
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human FGF10 consists of 172 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 19.6 kDa as estimated in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| Storage Condition | Samples are stable for up to twelve months from date of receipt at -70℃. Store it under sterile conditions at -20℃ to -80℃. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Purity | 98% as determined by SDS-PAGE |
More info
Protein Construction: A DNA sequence encoding the mature form of human FGF10 (NP_004456.1) (Gln 38-Ser 208) was expressed.
Formulation: Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, pH 7.51. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA.2. Please contact us for any concerns or special requirements.Please refer to the specific buffer information in the hard copy of CoA.
Reconstitution: A hardcopy of COA with reconstitution instruction is sent along with the products. Please refer to it for detailed information.
FGF10 Background Information: Fibroblast growth factor 1 (FGF1) is a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family. FGF family members possess broad mitogenic and cell survival activities, and are involved in a variety of biological processes, including embryonic development, cell growth, morphogenesis, tissue repair, tumor growth and invasion. FGF1 exhibits mitogenic activity for keratinizing epidermal cells, but essentially no activity for fibroblasts, which is similar to the biological activity of FGF7. FGF1 plays an important role in the regulation of embryonic development, cell proliferation and cell differentiation. FGF1 is required for normal branching morphogenesis. It may play a role in wound healing. Defects in FGF1 are the cause of autosomal dominant aplasia of lacrimal and salivary glands (ALSG). ALSG has variable expressivity, and affected individuals may have aplasia or hypoplasia of the lacrimal, parotid, submandibular and sublingual glands and absence of the lacrimal puncta. The disorder is characterized by irritable eyes, recurrent eye infections, epiphora (constant tearing) and xerostomia (dryness of the mouth), which increases the risk of dental erosion, dental caries, periodontal disease and oral infections.
References:
- Sekine K, et al. (1999) Fgf10 is essential for limb and lung formation. Nat Genet. 21(1): 138-41.
- Ohuchi H, et al. (2000) FGF10 acts as a major ligand for FGF receptor 2 IIIb in mouse multi-organ development. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 277(3): 643-9.
- Bellusci S, et al. (1997) Fibroblast growth factor 10 (FGF10) and branching morphogenesis in the embryonic mouse lung. Development. 124(23): 4867-78.

