No products
Product successfully added to your shopping cart
There are 0 items in your cart. There is 1 item in your cart.
Proteins and Enzymes
- Protein Control Ligand
- Pathway Inhibitors
- Enzyme Inhibitors
- Kinase Inhibitors
- Protease
- Synthase
- p18
- p38
- p53
- p70
- p90
- Peptidase
- Carboxyl and Decarboxylases
- Ceramide Turnover Enzymes
- Chromatin Modifying Enzymes
- Cyclic Nucleotide Turnover Enzymes
- Glycerophospholipid Turnover Enzymes
- Hydroxylases
- Ubiquitin-Activating Enzyme
- Adenosine Deaminase
- Clathrin
- Nuclease
- p68
- ACE
- COX
- DHFR
- Neprilysin
- NF-κB
- RAF
- RAS
- Reductase
- ROR
- Topoisomerase
- Transferase
- Protein Inhibitors
- Transporter Inhibitors
- Cell Inhibition
- Synthase
- Receptor Tyrosine Phosphatases (RTP)
- AChE
- Peptidase
- Autophagy
- Toll-Like Receptor (TLR)
- Enzyme Inhibitors
- Function Modulators
- Activators
- G Protein-Coupled Receptor Ligands
- 5HT Receptors
- Adrenoceptor
- Angiotensin Receptor
- Cannabinoid Receptors
- CCK Receptors
- DA Receptors
- EAA Receptors
- Ghrelin Receptors
- GABA Receptors
- Histamine Receptors
- Leukotriene Receptors
- Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors
- Motilin Receptors
- Muscarinic Receptor
- Neuropeptide Receptors
- Opioid Receptors
- Orexin Receptors
- Orphan Receptors
- Prostanoid Receptors
- Proteinase-Activated Receptors
- Purinergic Receptors
- Ryanodine receptor
- Sigma Receptors
- Thrombin Receptor
- Vaniloid Receptor
- VIP and PACAP Receptors
- Neurotensin Receptors
- Urotensin Receptor
- Imidazoline receptor
- SMO Receptors
- Apelin Receptor
- β-arrestin/β2-adaptin
- KDM4
- Glucocorticoid Receptor
- Laminin Receptor
- AHR
- Amylin Receptor
- Bombesin Receptor
- Bradykinin Receptor
- CFTR
- CGRP Receptor
- CRFR
- Endothelin Receptor
- Ephrin Receptor
- Farnesoid X receptor (FXR)
- Glucagon Receptor
- Nuclear Receptor Ligands
- GDNF Receptors
- TNF Receptors
- Transcription Factors
- Chemokines
- Cytokine Receptors
- Biomarkers and Buffer Solutions
- Molecular Probes
- Stem Cell Research
- Alzheimer's Disease
- Apoptosis
- Cancer Research
- Epigenetics
- Metabolites
- PET/SPECT Imaging Precursors
- Customized Screening Library
- Ultra Pure Pharmacological Standard
- Tissue Microarray (TMA)
- Proteins and Antibodies
- Primary Cells
- ELISA KIT
- Natural Products
- Lab Equipments
- Humanized Mice for PDX Platform
- Rare Chemicals
- Custom Synthesis
- Antibacterial
- Antifungal
- Antioxidant
- Antiviral
- Molecular Glues
- PROTAC Linker
- SARS-CoV
 View larger
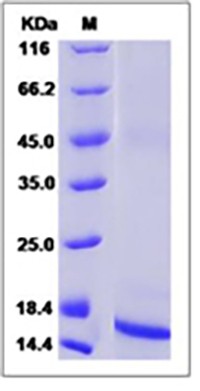
View larger Rat / Mouse TGF-beta 1 / TGFB1 Protein
80116-RNAH
Activity: Measured by its ability to inhibit cell proliferation of Mv-1-lu mink lung epithelial cells. The ED50 for this effect is 0.2-0.8 ng/mL.
1000 Items
Please ask for quote for unit smaller than 1 mg
Molarity Calculation Cart®
HOW TO ORDER
Data sheet
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant rat TGFB1 comprises 112 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 12.8 kDa. |
| Storage Condition | Samples are stable for up to twelve months from date of receipt at -70℃. Store it under sterile conditions at -20℃ to -80℃. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Purity | 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE |
More info
Protein Construction: A DNA sequence encoding the rat TGFB1 (Ala279-Ser390) was expressed. Rat and Mouse mature TGFB1 sequences are identical.
Formulation: Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.41. Normally 5% - 8% trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA.2. Please contact us for any concerns or special requirements.Please refer to the specific buffer information in the hard copy of CoA.
Reconstitution: A hardcopy of COA with reconstitution instruction is sent along with the products. Please refer to it for detailed information.
TGF beta 1 Background Information: TGF-beta 1 is a member of the transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) family. The transforming growth factor-beta family of polypeptides are involved in the regulation of cellular processes, including cell division, differentiation, motility, adhesion and death. TGF-beta 1 positively and negatively regulates many other growth factors. It inhibits the secretion and activity of many other cytokines including interferon-γ, tumor necrosis factor-alpha and various interleukins. It can also decrease the expression levels of cytokine receptors. Meanwhile, TGF-beta 1 also increases the expression of certain cytokines in T cells and promotes their proliferation, particularly if the cells are immature. TGF-beta 1 also inhibits proliferation and stimulates apoptosis of B cells, and plays a role in controlling the expression of antibody, transferrin and MHC class II proteins on immature and mature B cells. As for myeloid cells, TGF-beta 1can inhibit their proliferation and prevent their production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen intermediates. However, as with other cell types, TGF-beta 1 also has the opposite effect on cells of myeloid origin. TGF-beta 1 is a multifunctional protein that controls proliferation, differentiation and other functions in many cell types. It plays an important role in bone remodeling as it is a potent stimulator of osteoblastic bone formation, causing chemotaxis, proliferation and differentiation in committed osteoblasts. Once cells lose their sensitivity to TGF-beta1-mediated growth inhibition, autocrine TGF-beta signaling can promote tumorigenesis. Elevated levels of TGF-beta1 are often observed in advanced carcinomas, and have been correlated with increased tumor invasiveness and disease progression.
References:
- Ghadami M, et al. (2000) Genetic Mapping of the Camurati-Engelmann Disease Locus to Chromosome 19q13.1-q13.3. Am J Hum. Genet. 66(1):143-7.
- Letterio J, et al. (1998) Regulation of immune responses by TGF-beta. Annu Rev Immunol. 16:137-61.
- Vaughn SP, et al. (2000) Confirmation of the mapping of the Camurati-Englemann locus to 19q13. 2 and refinement to a 3.2-cM region. Genomics. 66(1):119-21.
- Assoian R, et al. (1983) Transforming growth factor-beta in human platelets. Identification of a major storage site, purification, and characterization. J Biol Chem. 258(11):7155-60.